Equilibrium points
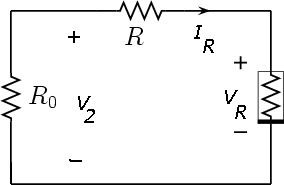
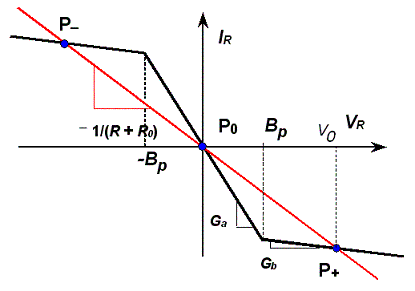
The equilibrium points are computed by setting to zero the derivatives in the state equations. That means that the capacitors are substituted by open circuits and the inductor by a short circuit, leading to the circuit of Fig. 1. Graphically, the equilibrium points are obtained by intersecting the "load line" of slope -1/(R + R0) with the Chua's diode characteristic.
|
|
With the parameter values used in the applet, apart of the equilibrium point P0 at the origin, the following two equilibrium points are obtained:
P+: VR = 4.282 V, IR = - 0.0021 A, V2 = 0.0298 V, corresponding to X+ = 3.965, Z+ = -2.604, Y+ = 0.02756
P-: VR = - 4.282 V, IR = 0.0021 A, V2 = - 0.0298 V, corresponding to X- = - 3.965, Z- = 2.604, Y- = - 0.02756
Last updated:
[Return to Home Page]